Is ketamine a "psychedelic"?

(2025) Psychedelics, derived from the Greek words "psyche" (soul) and "deloun" (revealing), are substances historically and currently considered "soul-revealing". Also termed hallucinogens due to their impact on sensory perception, they are further categorized into hallucinogens, such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), psilocybin, and mescaline; entactogens or empathogens, such as 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA); and dissociatives, such as phencyclidine (PCP) and ketamine. The concept of using these substances to enhance psychotherapy emerged in the 1940s, leading to the first wave of psychedelic research, which yielded promising initial results.

(2019) Classic serotonergic psychedelics are remarkable for their capacity to induce reversible alterations in consciousness of the self and the surroundings, mediated by agonism at serotonin 5-HT2Areceptors. The subjective effects elicited by dissociative drugs acting as N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists (e.g. ketamine and phencyclidine) overlap in certain domains with those of serotonergic psychedelics, suggesting some potential similarities in the brain activity patterns induced by both classes of drugs, despite different pharmacological mechanisms of action. We investigated source-localized magnetoencephalography recordings to determine the frequency-specific changes in oscillatory activity and long-range functional coupling that are common to two serotonergic compounds (lysergic acid diethylamide [LSD] and psilocybin) and the NMDA-antagonist ketamine. Administration of the three drugs resulted in widespread and broadband spectral power reductions. We established their similarity by using different pairs of compounds to train and subsequently evaluate multivariate machine learning classifiers. After applying the same methodology to functional connectivity values, we observed a pattern of occipital, parietal and frontal decreases in the low alpha and theta bands that were specific to LSD and psilocybin, as well as decreases in the low beta band common to the three drugs. Our results represent a first effort in the direction of quantifying the similarity of large-scale brain activity patterns induced by drugs of different mechanism of action, confirming the link between changes in theta and alpha oscillations and 5-HT2A agonism, while also revealing the decoupling of activity in the beta band as an effect shared between NMDA antagonists and 5-HT2A agonists. We discuss how these frequency-specific convergences and divergences in the power and functional connectivity of brain oscillations might relate to the overlapping subjective effects of serotonergic psychedelics and glutamatergic dissociative compounds.

(2020) " Using source-localised, steady-state MEG recordings, we describe changes in functional connectivity following the controlled administration of LSD, psilocybin and low-dose ketamine, as well as, for comparison, the (non-psychedelic) anticonvulsant drug tiagabine. We compare both undirected and directed measures of functional connectivity between placebo and drug conditions. We observe a general decrease in directed functional connectivity for all three psychedelics, as measured by Granger causality, throughout the brain. These data support the view that the psychedelic state involves a breakdown in patterns of functional organisation or information flow in the brain"


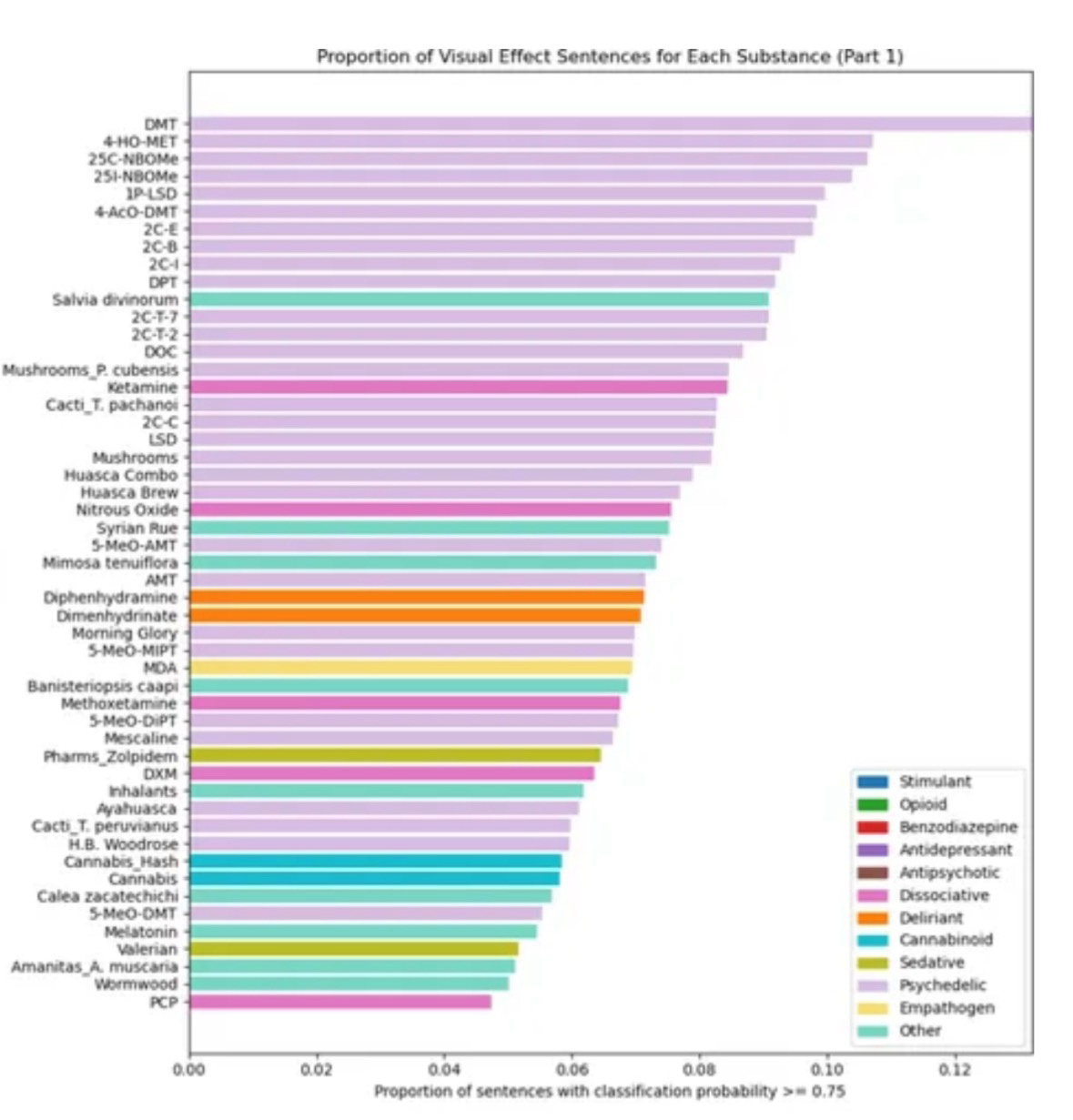






(2025) Psychedelics, a diverse group of psychoactive compounds, including LSD, psilocybin, DMT, MDMA, and ketamine, have shown potential in modulating neurologic and psychiatric disorders due to several mechanisms. This review investigates the therapeutic potential of psychedelics in both neurologic and neuropsychiatric disorders due to their several mechanisms such as anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, and biological properties.

(2025) The resurgence of psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy marks a pivotal evolution in mental health treatment, challenging traditional paradigms by integrating compounds such as psilocybin, LSD, MDMA, and ketamine into clinical practice.

(2025) Rapid-acting antidepressants such as ketamine and psilocybin offer promising alternatives, relieving symptoms within hours. Ketamine, an NMDA receptor antagonist, and psilocybin, a serotonergic psychedelic primarily targeting 5-HT2A receptors, both enhance synaptic plasticity in mood-regulating circuits through distinct mechanisms. This review synthesizes recent clinical and preclinical findings on ketamine and psilocybin, emphasizing their molecular targets, circuit-level effects, and converging downstream pathways. A key shared mechanism involves BDNF-TrkB signaling, which promotes spinogenesis and synaptogenesis critical for sustained antidepressant efficacy.

(2025) There is a signal that suggests ketamine could be used in a psychedelic therapy model with potential benefits over classical psychedelics.

(2025) This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluates (1) the effectiveness of psychedelic-assisted therapy (PAT) using psilocybin and ketamine for psychosocial symptoms in adults with cancer, (2) contextualizes findings with non-randomized and exploratory studies of other psychedelics, and (3) examines the role of therapeutic frameworks in shaping outcomes.

(2025) This trial found large and notably sustained benefits of ketamine-psychotherapy for severe TRD, with or without music, and psychedelic experiences of comparable intensity to those observed with psilocybin. Mystical-like experiences may particularly contribute to ketamine's immediate and persistent psychiatric benefits.

Ketamine produces an unusual state, sometimes referred to as “dissociative anesthesia”, which was a term coined by Domino’s (2010) wife.

(2024) Ketamine and SPs are associated with increased theta power in persons with depression. Ketamine and SPs are also associated with decreased spectral power in the alpha, beta and delta bands in healthy controls and persons with depression. When administered with SPs, theta power was increased in persons with MDD when administered with SPs. Ketamine is associated with increased gamma band power in both healthy controls and persons with MDD.

(2024) The aim of this review is to examine the emerging evidence-based data with regards to the therapeutic treatment of SUDs with the psychedelic compounds psilocybin, ketamine, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), ayahuasca, ibogaine and peyote.

(2024) Nine studies, involving 606 participants (362 treated with psychedelics: psilocybin, ketamine, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)) were included.

(2025) This review explores the potential of psychedelics, including psilocybin, LSD, and ketamine, as alternative therapeutic agents in chronic pain management.

(2025) This review examines how classic psychedelics (e.g., LSD, psilocybin, N,N-DMT) and non-classic psychedelics (e.g., ketamine, MDMA) influence neuroplasticity.

(2021) Through their primary glutamate or serotonin receptor targets, ketamine and psychedelics [psilocybin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), and N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT)] induce synaptic, structural, and functional changes, particularly in pyramidal neurons in the prefrontal cortex. These include increased glutamate release, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR) activation, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-mediated signaling, expression of synaptic proteins, and synaptogenesis. Such influences may facilitate adaptive rewiring of pathological neurocircuitry, thus providing a neuroplasticity-focused framework to explain the robust and sustained therapeutic effects of these compounds.

(2025) Psilocin increased synaptic puncta count and induced Arc expression. The effect to promote synaptogenesis was comparable to ketamine and lithium; ketamine additionally increased PSD-95 puncta count. LSD and DMT did not induce any significant effects.

(2023) Psychedelic compounds, including ketamine and LSD, have gained renewed interest as potential treatments for neuropsychiatric disorders. These compounds act as psychoplastogens, promoting neuronal growth by activating AMPA receptors, TrkB, and mTOR. The prefrontal cortex plays a crucial role in their therapeutic effects through top-down control over brain regions involved in motivation, fear, and reward. Some of these compounds exhibit antidepressant effects by enhancing synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis while also demonstrating anxiolytic properties through the modulation of fear circuits. Additionally, they show promise as anti-addictive agents by disrupting addictive patterns and promoting neuroplasticity. The exploration of how psychedelic substances can be therapeutically beneficial reveals new opportunities for addressing conditions like major depressive disorder, anxiety, and addiction.

(2024) Psychedelic drugs such as psilocybin and ketamine are returning to clinical research and intervention across several disorders including the treatment of depression.

(2023) Ketamine, MDMA, LSD and psilocybin were selected for comparison due to their promising therapeutic effects and different mechanisms of action. This study aimed to (a) identify factors that produce positive and adverse psychedelic experience, and (b) compare these potential predictors across four psychedelic substances.

(2023) We conducted a scoping review of pipeline clinical trials of psychedelic treatment for depression, anxiety, and existential distress at end of life... Investigational drugs included ketamine (n = 11), psilocybin (n = 10), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (n = 2), and lysergic acid diethylamide (n = 2). Three trials involved microdosing, and fifteen trials incorporated psychotherapy.


(2023) To bridge these different levels of observation, we have here performed large-scale multi-structure recordings in freely behaving rats treated with 5-HT2AR psychedelics (LSD, DOI) and NMDAR psychedelics (ketamine, PCP).

(2023) We analyzed whole-brain functional connectivity based on resting-state fMRI data in humans, acquired before and during the administration of nitrous oxide, ketamine, and lysergic acid diethylamide. We report that, despite distinct molecular mechanisms and modes of delivery, all three psychedelics reduced within-network functional connectivity and enhanced between-network functional connectivity. More specifically, all three drugs increased connectivity between right temporoparietal junction and bilateral intraparietal sulcus as well as between precuneus and left intraparietal sulcus. These regions fall within the posterior cortical "hot zone," posited to mediate the qualitative aspects of experience. Thus, both classical and non-classical psychedelics modulate networks within an area of known relevance for consciousness, identifying a biologically plausible candidate for their subjective effects.

(2023) The classic serotonergic psychedelics psilocybin and lysergic acid diethylamide and nonclassic psychedelics 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine and ketamine are increasingly appreciated as neuroplastogens given their potential to fundamentally alter mood and behavior well beyond the time window of measurable exposure. Imaging studies with psychedelics are also helping advance our understanding of neural networks and connectomics. This resurgence in psychedelic science and psychedelic-assisted therapy has potential significance for the fields of neurosurgery and neuro-oncology and their diverse and challenging patients, many of whom continue to have mental health issues and poor quality of life despite receiving state-of-the-art care.

(2023) The opposite harmonic signature characterises the altered state induced by LSD or ketamine, reflecting psychedelic-induced decoupling of brain function from structure and correlating with physiological and subjective scores.
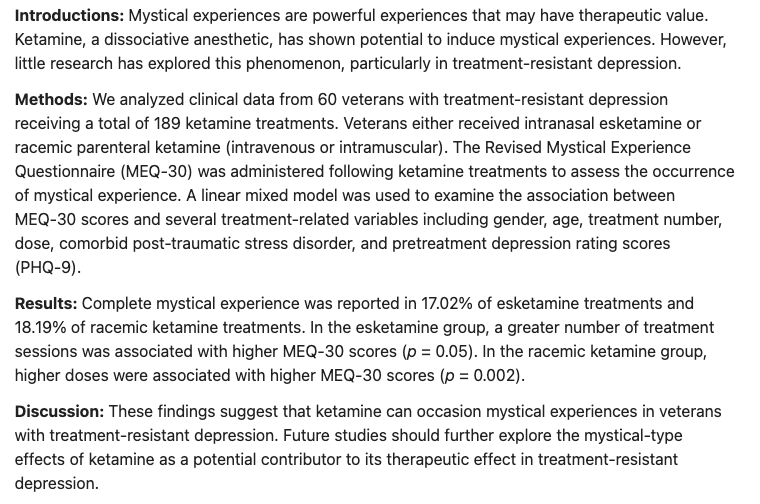
(2025): "These findings suggest that ketamine can occasion mystical experiences in veterans with treatment-resistant depression. Future studies should further explore the mystical-type effects of ketamine as a potential contributor to its therapeutic effect in treatment-resistant depression."

(2021):"We found that ketamine leads to significantly greater mystical-type effects (by Hood Mysticism Scale) and dissociation (by Clinician Administered Dissociative States Scale) compared to the active control. Ketamine also led to significant reduction in at-risk drinking. The Hood Mysticism Scale, but not Clinician Administered Dissociative States Scale score, was found to mediate the effect of ketamine on drinking behavior."

(2025): "Ketamine is an evidenced-based treatment for depression, and it has shown promise in addressing many other mental health conditions related to work-related stress or burnout, such as anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder. Ketamine-assisted psychotherapy (KAP) is part of an emerging model of psychedelic medicine that employs psychoactive agents to support the psychotherapeutic process."
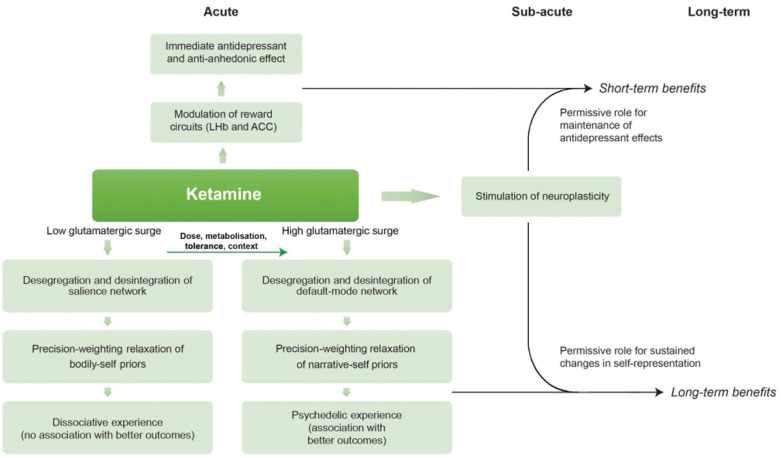
(2022): "...ketamine is also commonly classified as an atypical psychedelic and it has been recently reported that ego dissolution experiences during ketamine administration are associated with greater antidepressant response. Neuroimaging studies have highlighted several similarities between the effects of ketamine and those of serotonergic psychedelics in the brain..."

(2024): "While much of the literature on ketamine labels its dissociative effects as ‘side effects’, alteration of consciousness is a component and unavoidable ‘effect’ of its therapeutic impact. From its inception in the clinical trials of the 1960s, ketamine was recognized for producing dissociative, psychedelic effects on consciousness in subjects as they emerged from ketamine-induced anesthesia.


(2016): "Some of ketamine’s more profound effects, which are generally occasioned at higher but sub-anesthetic doses, include the simulation of a near-death experience, the complete dissolution of the identity of the participant, and visionary states that can occur with other psychedelic molecules. Given the potentially profound and singular nature of the ketamine psychedelic experience, the meaning-making that can be derived from such experiences can effect a radical transformation of an individual’s worldview."


(2025): "the connectome harmonic repertoire under N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is reshaped in line with other reported psychedelic compounds - psilocybin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and ketamine. Furthermore, we show that the repertoire entropy of connectome harmonics increases under DMT, as with those other psychedelics. "

(2025): "Psychedelics, such as psilocybin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), ketamine, and N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT), have captured the attention of scientists, artists, and seekers alike for their profound ability to alter consciousness and inspire creativity."

(2025): "much like the serotonergic psychedelics, the authors concluded that ketamine could improve psychotherapeutic treatments and facilitate mental health practitioner training."












































